Block Diagram Examples Control System
Block diagram examples control system. Consider the generic cubic polynomial. Next we consider the fourth-order polynomial. A Block Diagram is a shorthand pictorial representation of the cause-and-effect relationship of a system.
The relative node placement feature makes it a bit easier but it works best when the nodes have equal widths. Worrying about how to solve block diagram reduction examples and finding transfer function then you are at right place watch this video till end and you will. Example 9 Find the transfer function of the following block diagrams 2G 3G1G 4G 1H 2H sY.
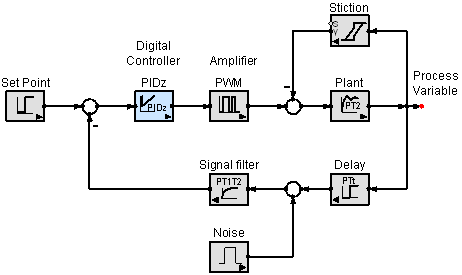
However the results are quite pleasing and hopefully worth the effort. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure. The interior of the rectangle representing the block usually contains a description of or the name of the element gain or the symbol for the mathematical operation to.
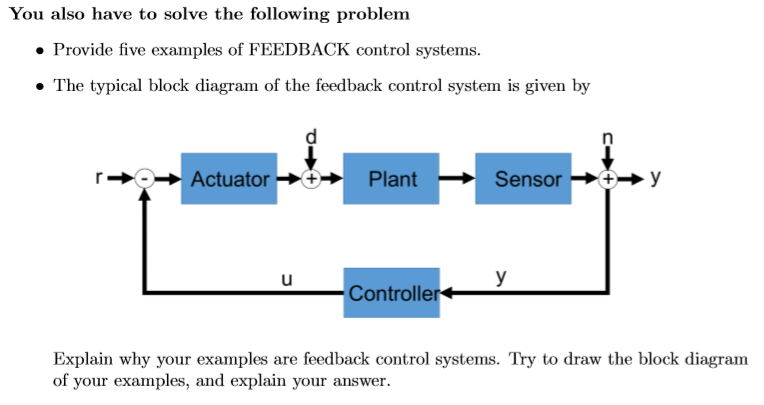
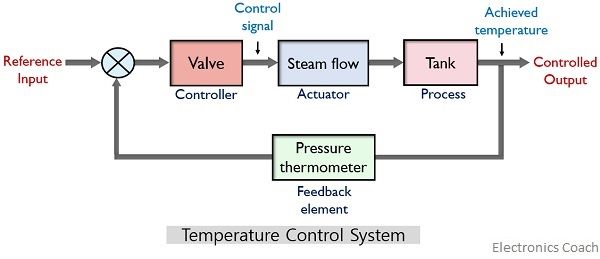
An open-loop control system is one in which the control action is independent of the output. It will include block diagram reduction rules some block diagram reduction examples and solutions. Block diagrams like this are quite time consuming to create by hand.
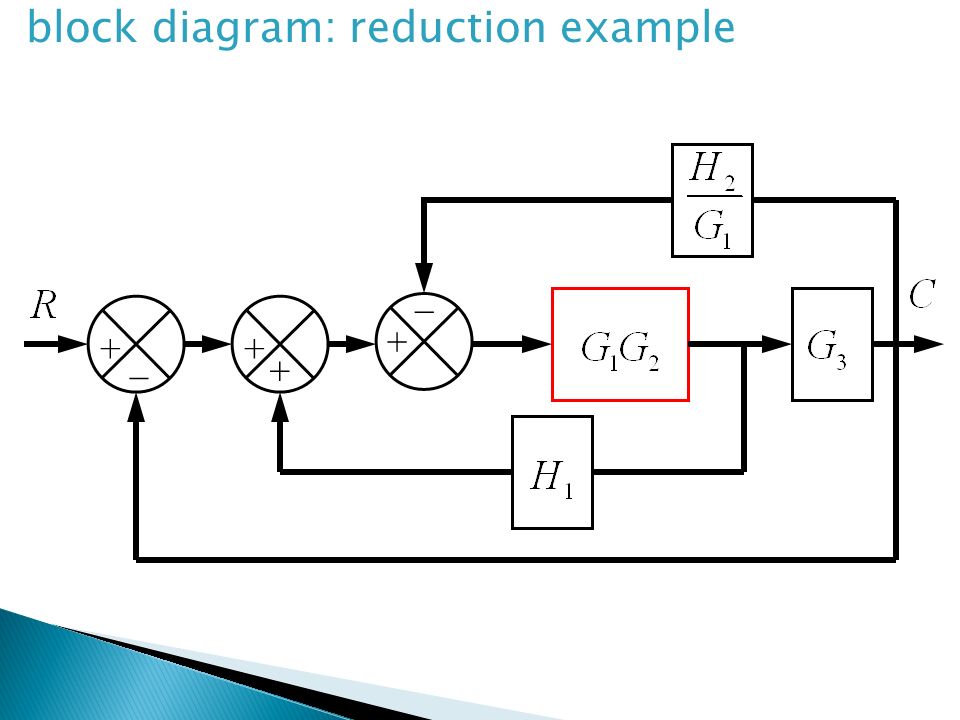
Block Diagram Simplification Example 1 Rearrange the following into a unity -feedback system Move the feedback block 𝐻𝐻𝑠𝑠 forward past the summing junction Add an inverse block on 𝑅𝑅𝑠𝑠to compensate for the move Closed-loop transfer function. Boxes that represents the components of the system including their causality. Basic Elements of Block Diagram.
The block diagram of the car speed control system Kp Ki D ----- KdD 10 vdesired verror θgas F vactual -1 MD-----Kp Ki D ----- KdD vdesired verror θgas vactual -10 MD-----Kp Ki D. S4 2s3 3s2 4s5 0. First move the branch point of the path involving HI outside the loop involving H as shown in Figure 3-43a.
Figure 817 An example of simplifying a block diagram The function block is further simplified in Figure 818 to a final transfer function for the whole system. Then eliminating two loops results in Figure 3-43b.
Worrying about how to solve block diagram reduction examples and finding transfer function then you are at right place watch this video till end and you will.
Basic Elements of Block Diagram. However the results are quite pleasing and hopefully worth the effort. Bishop Modern Control Systems 11th Ed Pearson Prentice-Hall 2008. Consider the generic cubic polynomial. Block diagrams are used to simplify complex control systems. Control System Engineering Kuntumal Sagar M. A 0s 3 a 1s 2 a 2sa 3 0 14 where all the a i are positive. EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS A-3-1. We know that the input-output behavior of a linear system is given by its transfer function.
Then eliminating two loops results in Figure 3-43b. Using block diagram reduction find the transfer function Y s R. A 0s 3 a 1s 2 a 2sa 3 0 14 where all the a i are positive. Example 9 Find the transfer function of the following block diagrams 2G 3G1G 4G 1H 2H sY. Draw the block diagram of the control system for the following cases. Consider the generic cubic polynomial. The block diagram of the car speed control system Kp Ki D ----- KdD 10 vdesired verror θgas F vactual -1 MD-----Kp Ki D ----- KdD vdesired verror θgas vactual -10 MD-----Kp Ki D.





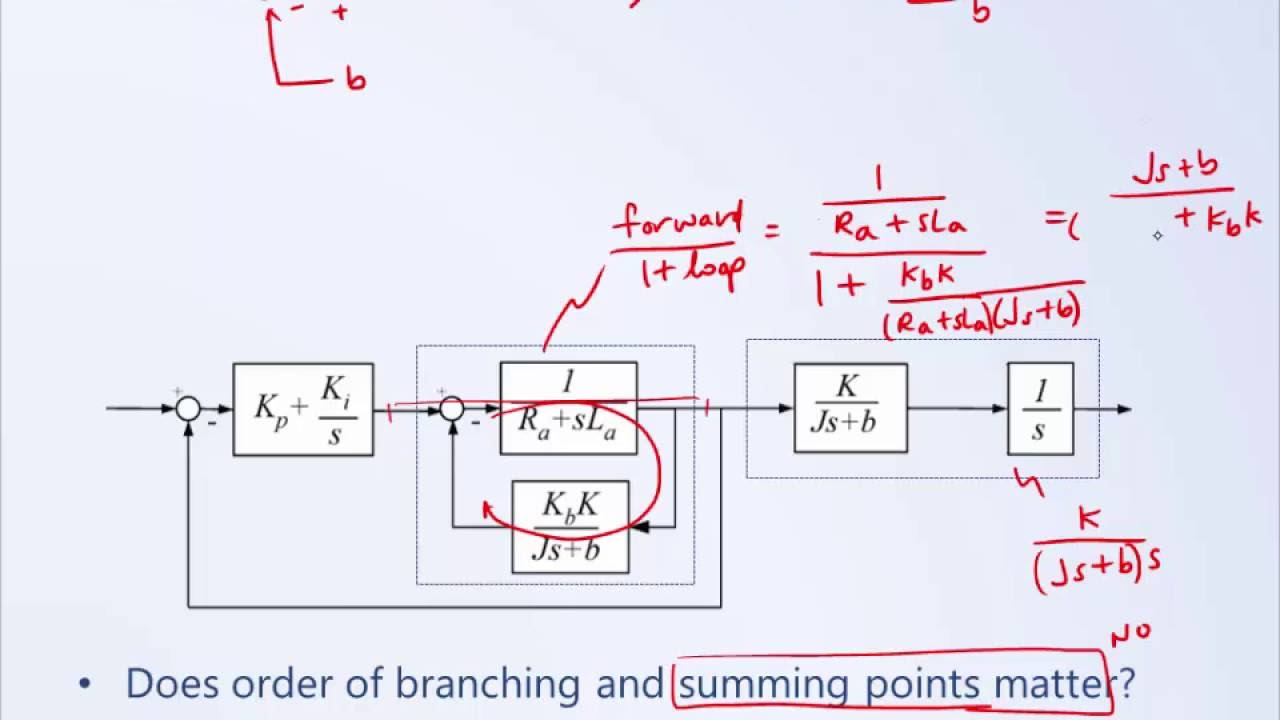
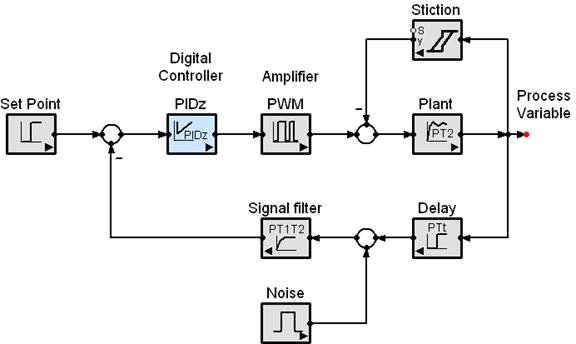


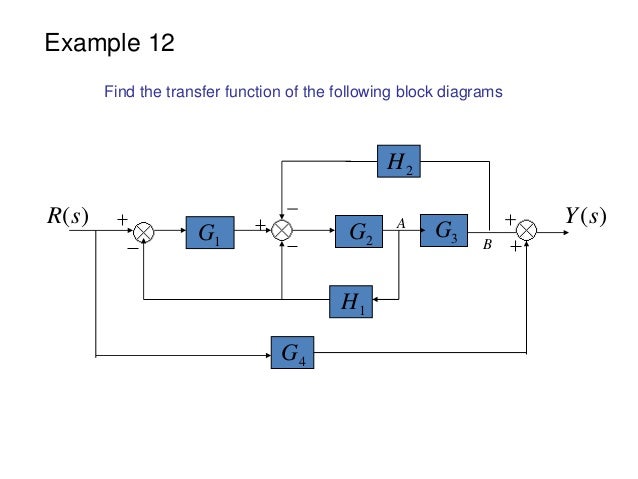

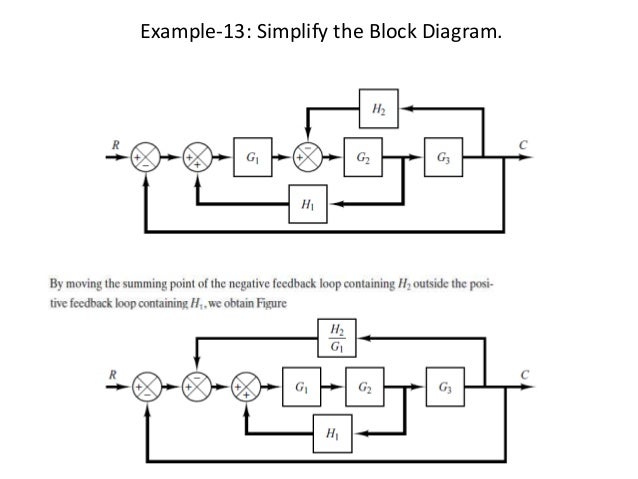

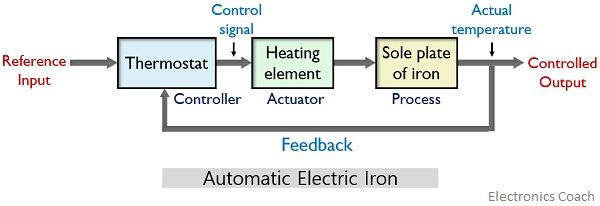




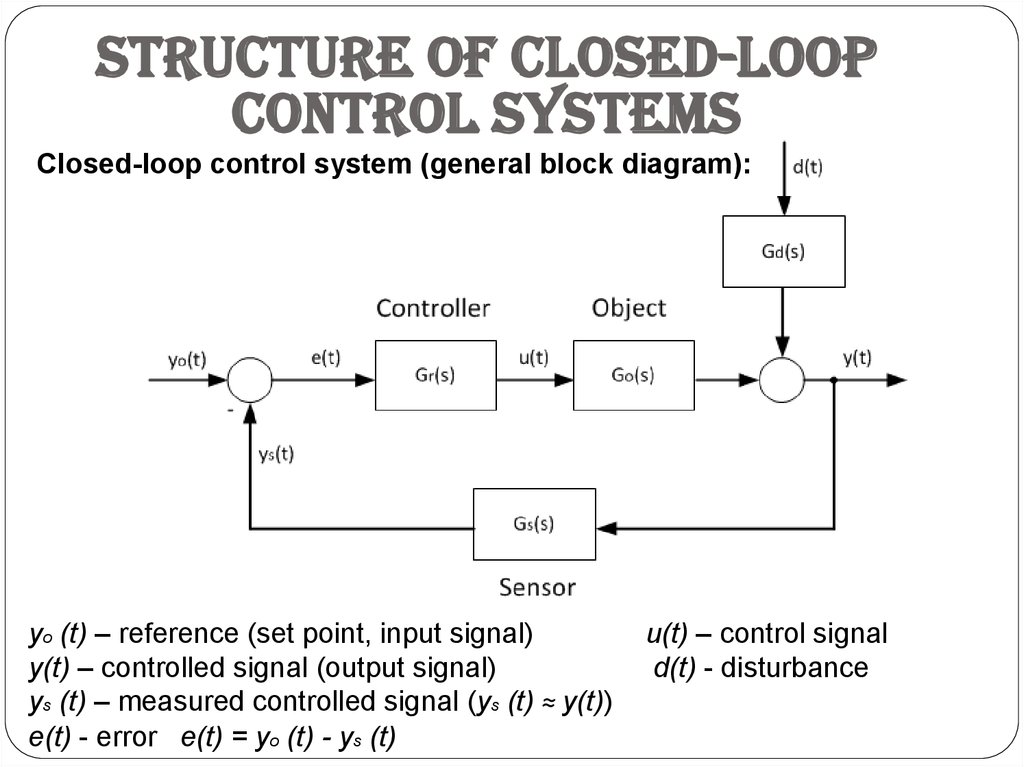



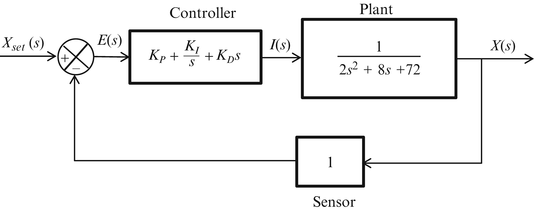


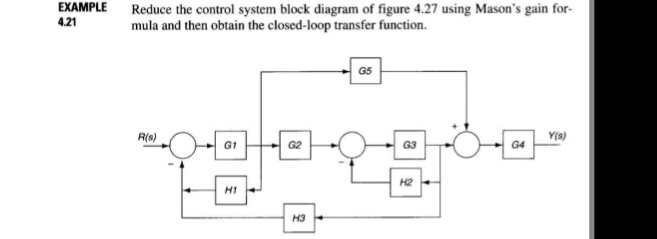



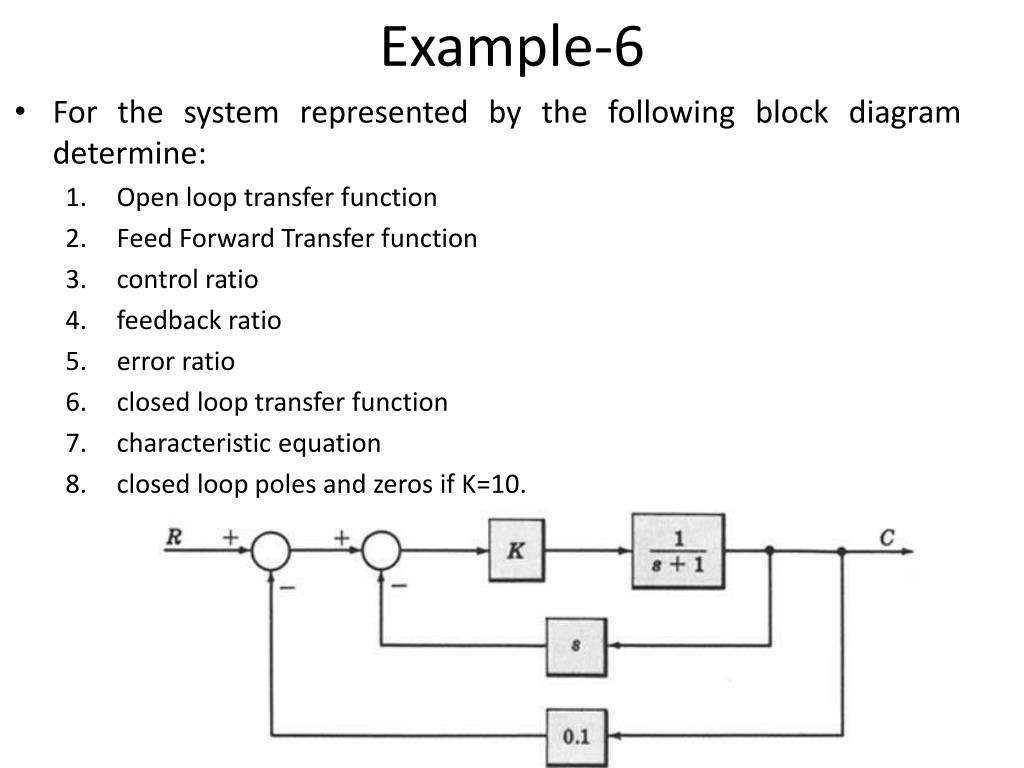

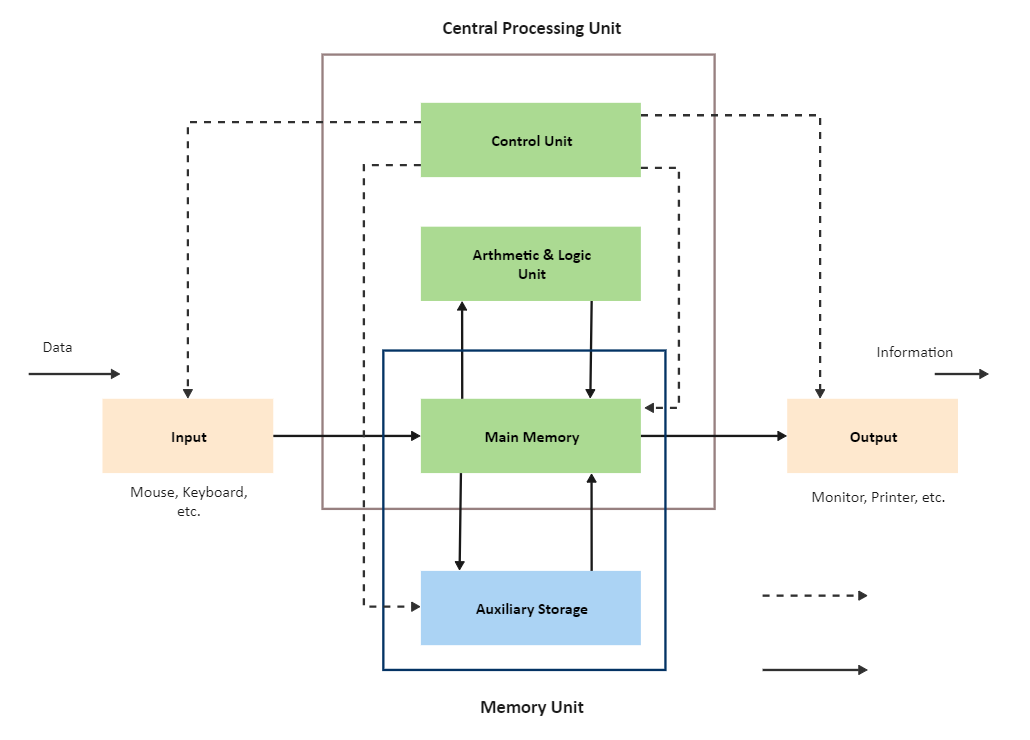
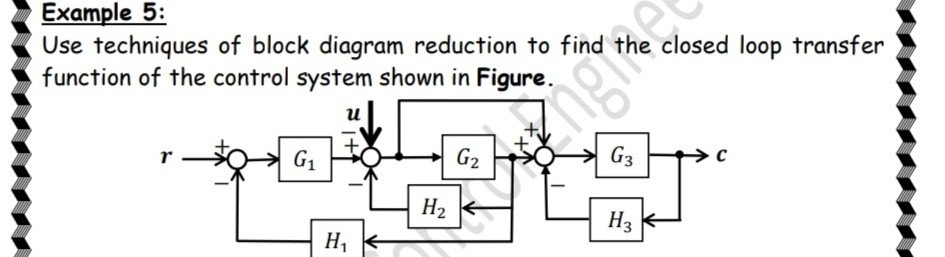



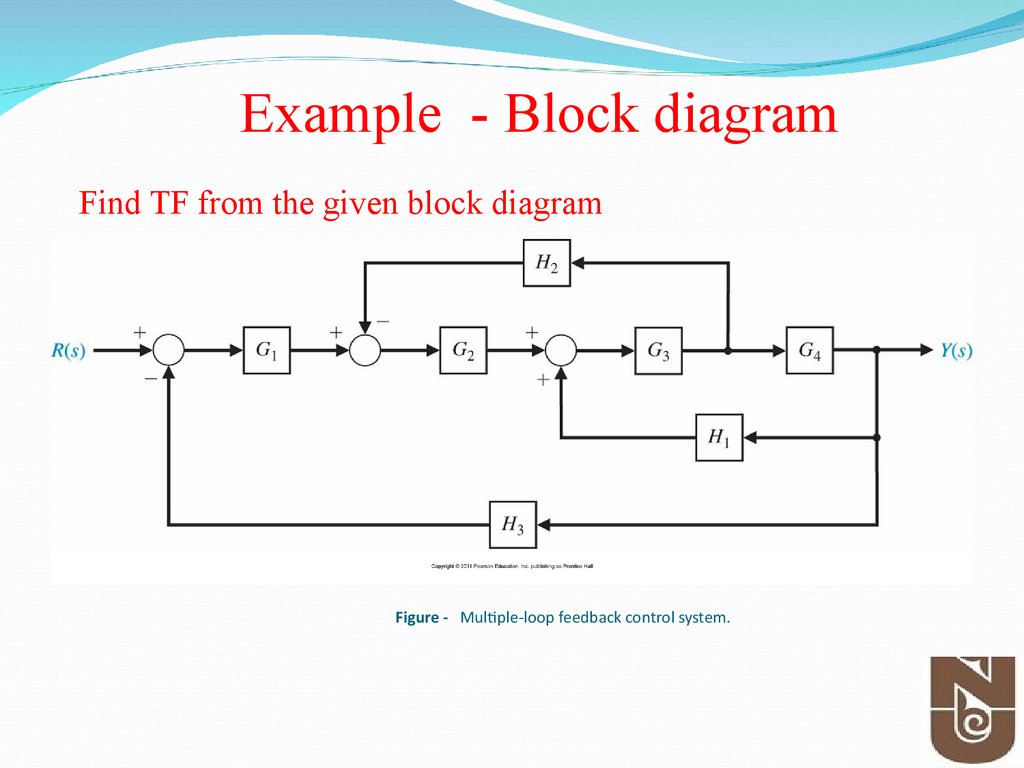


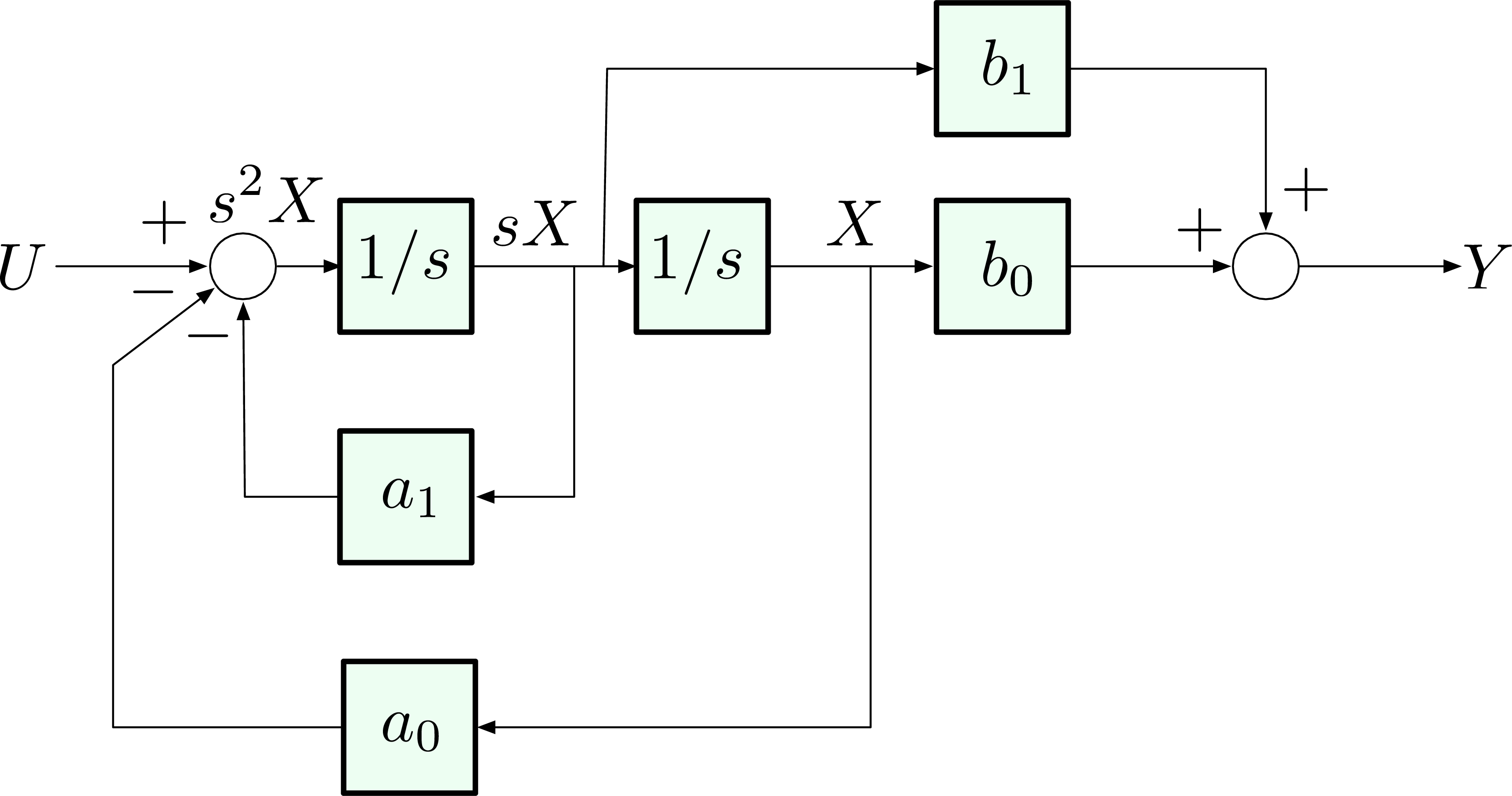
Post a Comment for "Block Diagram Examples Control System"